1. 初中数学中的不变量
Posted by haifeng on 2024-05-31 08:58:06 last update 2024-05-31 08:58:06 | Answers (0) | 收藏
1. 凸多边形的外角和等于 $360^{\circ}$.
Posted by haifeng on 2024-05-31 08:58:06 last update 2024-05-31 08:58:06 | Answers (0) | 收藏
1. 凸多边形的外角和等于 $360^{\circ}$.
Posted by haifeng on 2022-03-26 07:53:18 last update 2022-03-26 09:10:33 | Answers (0) | 收藏
规范场理论(Gauge Theory)
参考资料
D. S. Freed, K. K. Uhlenbeck: Instantons and four-Manifolds.
H. B. Lawson, Jr.: The theory of gauge fields in four-dimension.
K. Donaldson & Kronheimer: Geometry of Four-Manifolds.
几何参考书
K. Kobayashi, K. Nomizu, Foundations of Differential Geometry.
J. Milnor, J. Stasheff, Characteristic classes.
N. Steenord, The topology of Fibre Bundles.
Aubin, Nonlinear Problems in Riemann manifolds.
Atiya, K-theory.
Posted by haifeng on 2021-06-28 07:18:21 last update 2021-06-28 09:44:42 | Answers (0) | 收藏
[分析]
Y: Sunrise Time (LST)
Y2=X2-W2*4/1440
Z: Sunset Time (LST)
Z2=X2+W2*4/1440
X: Solar Noon (LST)
X2=(720-4*$b$4-V2+$B$5*60)/1440
这里 $B$4 : longitude, $B$5: timezone
V: Equation of time (时差) 单位: minutes
V2=4*DEGREES(U2*SIN(2*RADIANS(I2))-2*K2*SIN(RADIANS(J2))+4*K2*U2*SIN(RADIANS(J2))*COS(2*RADIANS(I2))-0.5*U2*SIN(4*RADIANS(I2))-1.25*K2*K2*SIN(2*RADIANS(J2)))
即,
\[
\begin{split}
V2&=4\cdot\Bigl[U2\cdot\sin(2\cdot I2)-2\cdot K2\cdot\sin(J2)+4\cdot K2\cdot U2\cdot\sin(J2)\cdot\cos(2\cdot I2)\\
&\quad -\frac{1}{2}\cdot U2\cdot\sin(4\cdot I2)-\frac{5}{4}\cdot K2\cdot K2\cdot\sin(2\cdot J2)\Bigr]
\end{split}
\]
I. (Geom Mean Long Sun) (deg)
I2=MOD(280.46646+G2*(36000.76983+G2*0.0003032),360)
J. (Geom Mean Anom Sun) (deg)
J2=357.52911+G2*(35999.05029-0.0001537*G2)
G. Julian Century
G2=(F2-2451545)/36525
这里 2451545 对应到 2000年1月1日.
F. Julian Day(儒略日)
\[
F2=D2+2415018.5+E2-$B$5/24
\]
$B$5 是 Time Zone (+ to E), E指 East.
D, Date, D2=$B$7, 如: 2010/6/21
Julian Day
For example: The Julian day number for the day starting at 12:00 UT on January 1, 2000 was 2,451,545.
E. Time (past local midnight). 从午夜开始经过的时间
\[
E(i+1)=E(i)+0.1/24,\quad E(2)=0.1/24
\]
240行, 24h/240=0.1h=6min
所以
\[
\begin{split}
F2&=D2+2415018.5+E2-\$B\$5/24\\
&=2010/6/21+2415018.5+0:06:00-1/24\\
&=2455368.75
\end{split}
\]
这推出 $2010/6/21+0:06:00\approx 40350.29166667$.
儒略日(Julian Day) 的起点定在公元前 4713 年(天文学上记为 $-4712$ 年)1月1日格林威治时间平午(世界时间12:00). 即 JD 0 指定为 4713 B.C. 1月1日 12:00 UT 到 4713 B.C. 1月2日 12:00 UT 的 24 小时. 每一天赋予了一个唯一的数字, 顺数而下.
如: 1996年1月1日12:00:00的儒略日是 2450084
1899年12月29日 --- 2415018
这个日期是考虑了太阳、月亮的运行周期, 以及当时税收的间隔而定下来的.
Joseph Scliger 定义儒略周期为 7980年. $7980=\text{l.c.m.}(19,15,28)$.
28年为一太阳周期(Solar cycle). 经过一太阳周期, 则星期的日序与月的日序会重复.
19年为一太阴周期, 或称默冬章(Metonic cycle), 因235朔望月=19回归年, 经过一太阴周期则阴历月年的日序重复.
15年为一小纪(indiction cycle), 此为罗马皇帝君士坦丁(Constantine)所颁, 每15年评定财产价值以供课税, 成为古罗马用的一个纪元单位.
故以7980年为一儒略周期, 而所选的起点公元前4713年, 则是这三个循环周期同时开始的最近年份.
注: 7980 是这三个数的最小公倍数.
>> lcm(28,19,15)
in> lcm(28,19,15)
7980
\[
\begin{aligned}
a&=\bigl[(14-\text{month})/12\bigr]\\
y&=\text{year}+4800-a\\
m&=\text{month}+12a-3
\end{aligned}
\]
则格里历日期的中午时候
\[
\text{JDN}=\text{day}+\bigl[(153m+2)/5\bigr]+365y+[y/4]-[y/100]+[y/400]-32045,
\]
若日期为儒略历, 则
\[
\text{JDN}=\text{day}+\bigl[(153m+2)/5\bigr]+365y+[y/4]-32083.
\]
儒略日的简化
\[
\text{MJD}=\text{JD}-2400000.5
\]
U
(var y)
U2=TAN(RADIANS(R2/2))*TAN(RADIANS(R2/2))
即, $U2=\tan^2\frac{R_2}{2}$.
R (Obliq Corr) (deg)
R2=Q2+0.00256*COS(RADIANS(125.04-1934.136*G2))
即
\[
R_2=Q_2+0.00256\cdot\cos(125.04-1934.136\cdot G_2)
\]
Q. (Mean Obliq Ecliptic) (deg)
Q2=23+(26+((21.448-G2*(46.815+G2*(0.00059-G2*0.001813))))/60)/60
K. Eccent Earth Orbit (eccentricity of earth) 地球的离心率
K2=0.016708634-G2*(0.000042037+0.0000001267*G2)
[待修改]
References:
https://blog.csdn.net/caolaosanahnu/article/details/7890008
Julian Day Number Calculations (numerical.recipes)
Posted by haifeng on 2020-09-22 11:04:52 last update 2020-09-22 11:22:27 | Answers (0) | 收藏
$T\in D_n(U)$ 称为一个 rectifiable current, 如果对所有的 $\omega\in D^n(U)$, 有
\[
T(\omega)=\int_M\langle\omega(x),\xi(x)\rangle\theta(x)\mathrm{d}H^n(x)
\]
这里 $M$ 是 $U$ 中的 $H^n$-可测的可数 $n$-rectifiable 子集.
$\theta$ 是局部 $H^n$-可积的正函数 (叫做重数函数).
$\xi:\ M\rightarrow\Lambda_n\mathbb{R}^p$ 是一个 $H^n$-可测函数, 满足下面的关系: 在几乎处处 $H^n$-可测的点 $x\in H$ 处(at $H^n$-a.e. $x\in H$), 有 $\xi(x)=\tau_1\wedge\cdots\wedge\tau_n$, 其中 $\{\tau_1,\ldots,\tau_n\}$ 是 $T_x M$ 的一个标准正交基.
记 $T=\tau(M,\theta,\xi)$.
若 $\theta$ 是取整数值的, 则这样的 current 被称为是一个整数可乘性的 rectifiable current. (an integer multiplicity rectifiable current)
定理. 若 $V\subset U\subset\mathbb{R}^{n+1}$ 具有局部有限的周边(locally finite perimeter), 即 $\chi_V\in\mathrm{BV}_{loc}(U)$, 则 $\partial [[V]]$ 是一个 integer multiplicity current, 满足 $\theta(x)=1$ 对 $H^n-$ a.e. $x\in M$.
Reference:
来源于笔记
Posted by haifeng on 2017-05-08 23:40:16 last update 2017-05-12 09:44:08 | Answers (2) | 收藏
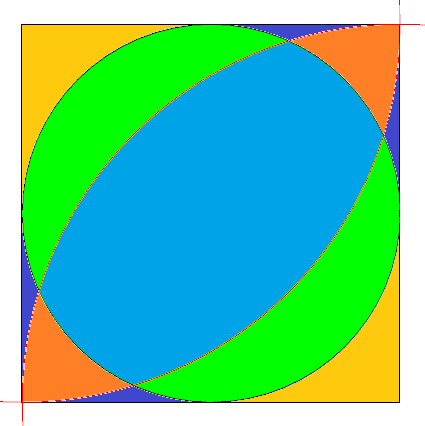
假设正方形的边长是 10, 求图中绿色部分的面积.
Answer: 单个的绿色部分面积为
\[25\arccos\frac{1}{2\sqrt{2}}-100\arccos\frac{5}{4\sqrt{2}}+\frac{25}{2}\sqrt{7}\]
题目来源: Lei Liu (刘磊)
Posted by haifeng on 2012-06-04 13:11:50 last update 2012-06-04 13:17:45 | Answers (0) | 收藏
证明.
\[\text{Vol}(S^{2n-1})=\frac{2\pi^n}{(n-1)!}\]
\[\text{Vol}(S^{2n})=\frac{2^{n+1}\pi^n}{(2n-1)!!}\]
注意.
$S^{2n-1}$ 的球坐标为
\[\begin{cases}x_1&=\cos\theta_1\\ x_2&=\sin\theta_1\cos\theta_2\\ x_3&=\sin\theta_1\sin\theta_2\cos\theta_3\\ &\vdots\\ x_{2n-1}&=\sin\theta_1\sin\theta_2\cdots\sin\theta_{2n-2}\cos\theta_{2n-1}\\ x_{2n}&=\sin\theta_1\sin\theta_2\cdots\sin\theta_{2n-2}\sin\theta_{2n-1}\end{cases}\]
$S^{2n}$ 的球坐标为
\[\begin{cases}x_1&=\cos\theta_1\\ x_2&=\sin\theta_1\cos\theta_2\\ x_3&=\sin\theta_1\sin\theta_2\cos\theta_3\\ &\vdots\\ x_{2n}&=\sin\theta_1\sin\theta_2\cdots\sin\theta_{2n-1}\cos\theta_{2n}\\ x_{2n+1}&=\sin\theta_1\sin\theta_2\cdots\sin\theta_{2n-1}\sin\theta_{2n}\end{cases}\]
Posted by haifeng on 2011-04-02 19:39:24 last update 2012-09-01 19:32:44 | Answers (1) | 收藏